More traffic today is going over wireless networks than ever before. For years, wireless networks have provided connections wherever your employees need to work – at their desks, in conference rooms, at home, on warehouse floors or at another office location.
WiFi Technology, Standards and Protocols
As wireless networks have evolved, so have wi-fi technology, standards, and protocols.
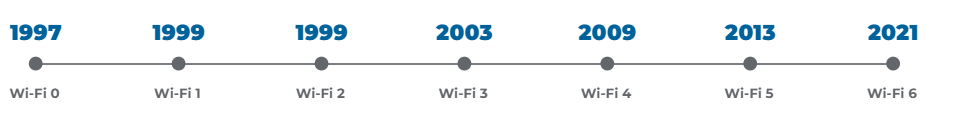
WiFi standards are set by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). Over time, different classifications of WiFi networks were given different naming conventions to help make it easier for consumers to understand. Today we can just look for WiFi 1 through 6, with WiFi 6 being the standard.
There are a number of acronyms for the different varieties of WiFi networks, but they all basically mean a few things:
- How far can the wireless signal reach
- How much data can the signal send
- Is it backwards compatible with other standards
Emerging Technology
WiFi 7, the next generation, has recently released and promises faster connections, lower latency and the ability to manage more connections. The WiFi Alliance predicts that 233 million Wi-Fi 7 devices will enter the market in 2024 and grow to 2.1 billion devices by 2028.
New Era of Wireless Complexity
In an era defined by digital transformation, the role of wireless connectivity has transcended from a convenience to an absolute necessity. As businesses adapt to the digital era, wireless connectivity has emerged as THE key for success.
However, the surge in users, IoT devices, automation, and new applications has ushered in a new era of complexity, IT professionals have their hands full just keeping track of everything on the wireless network — never mind securing it all.
How does wireless security work?
Wireless security primarily concerns itself with traffic that travels over the air between wireless devices. These include wireless access points (APs) communicating with a controller device, as well as communications between APs and endpoints connected to the Wi-Fi network.
Encryption is one of the most important tools used to create a secure network. Data encryption has been a part of securing networks from the very beginning. Over the years, wireless encryption standards have evolved in response to changing network requirements, emerging security issues and the discovery of vulnerabilities in prior encryption protocols.
Important steps to secure your wireless network.
1. Encryption
Using encryption is the first and most basic step of securing your wireless network. To do so, you will need to access the security settings for your router. Look for the options to encrypt the signal, these will include WEP, WPA and WPA2 and WPA3.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a security standard for computing devices with wireless internet connections. It was developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to provide better data encryption and user authentication than Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), which was the original Wi-Fi security standard.
Since the late 1990s, Wi-Fi security types have gone through multiple evolutions to improve them.
When choosing from among WEP, WPA, WPA2 and WPA3 wireless security protocols, experts agree WPA3 is best for Wi-Fi security. As the most up-to-date wireless encryption protocol, WPA3 is the most secure choice. Some wireless APs do not support WPA3, however. In that case, the next best option is WPA2, which is widely deployed in the enterprise space today.
2. Hide your Network
The SSID is essentially the name of your wireless network. When your router is set to broadcast the SSID, it provides devices that are searching for a wireless network, with the name of your connection. If a person can identify your network, this gives them the first piece of information that they will need to access it. With this feature disabled, any person that wants access to your network will need to find the name of the connection before they can start trying to hack your password. This creates another layer of protection.
3. Set a strong password for your Wi-Fi router
Every router has a password to allow for administrative access. This is where you adjust how the network operates, or to change settings such as the encryption. The problem is that with most wireless routers, the default username and password will be something simple and easy for an outside individual to figure out. Go to the security settings on your router, and change the password to a longer password that includes a mix of upper- and lowercase letters, characters, and symbols.
4. Limit Physical Access to Wireless Equipment
Even with all of the above steps, it may still be possible for a determined individual to gain access to your network. Enterprise wireless routers and access points should be in secure locations such as locked wiring closets.
5. Utilize a VPN
Virtual Private Networks (VPN) have been around for years and continue to evolve over time. A VPN is a software solution that minimizes the security risks of using Wi-Fi by creating an encrypted channel, often referred to as a tunnel, that connects your device to the internet via a private proxy server.
When choosing a VPN solution for your business or personal use, consider these features:
- Strong encryption algorithms: most VPNs use AES-256 bit encryption
- Robust support for authentication
- Support for logging, auditing, and digital certificate
- Inclusion of a kill switch, which ensures that whenever a VPN connection is lost, either the internet connection is shut down or the apps using the connection stop operating.
Evolve and Secure Your Wireless Technology Today
If you’re looking to improve and secure the wireless technology for your business and employees, we can help you achieve seamless communication, fast information access and secure connections. Contact DWD’s network team today for a free network evaluation.
